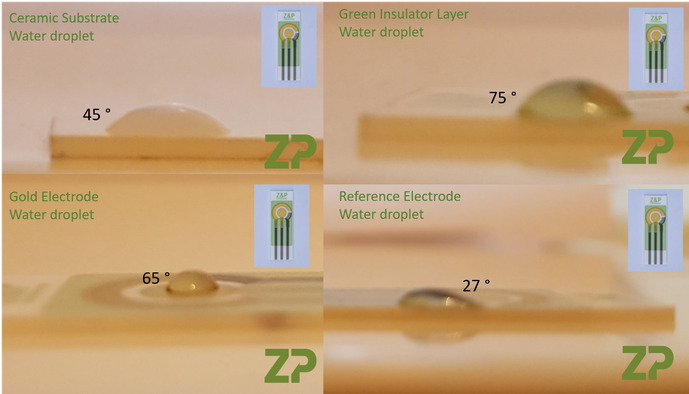
Wettability of the sensor's materials of construction
In the images below we have assessed the wettability of gold sensors with water and ethanol. When looking at the contact angles for water one could say that an aqueous drops may prefer wetting the ceramic substrate, rather than being retained upon the gold electrodes. The contact angle of the the water droplet on the green insulator would suggest that the spill barrier on some of our standard sensors could be effective for retaining a solution on the gold electrodes when the drop is aqueous in nature.. Click the link to see an example of a spill barrier - click here .
When one considers the images of the ethanol drop it is apparent that the ethanol is very good at wetting most of the materials on the sensor. If one wishes to contain a solution on an electrode when the solution is organic in nature it may be prudent to use a more substantial barrier as discussed in the following link - click here.
In the image opposite we have determined the contact angle for a water droplet on the surfaces of some of our gold electrodes - click here.
In the image opposite we have determined the contact angle for an ethanol droplet on the surfaces of some of our gold electrodes - click here.
